https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/e/2PACX-1vSAY3Jp5PCA77R3-F6WR_-9U9gjL-kZ1F-7rbu1ngz88Mi49W0iEgV3ssQw1b_BCQ/pubembed?start=false&loop=false&delayms=3000
Este tutorial apresenta um fluxo completo de trabalho em Google Colab para implementar modelos clássicos com Scikit-learn e uma rede neural básica com TensorFlow. Ao final, você terá código executável para:
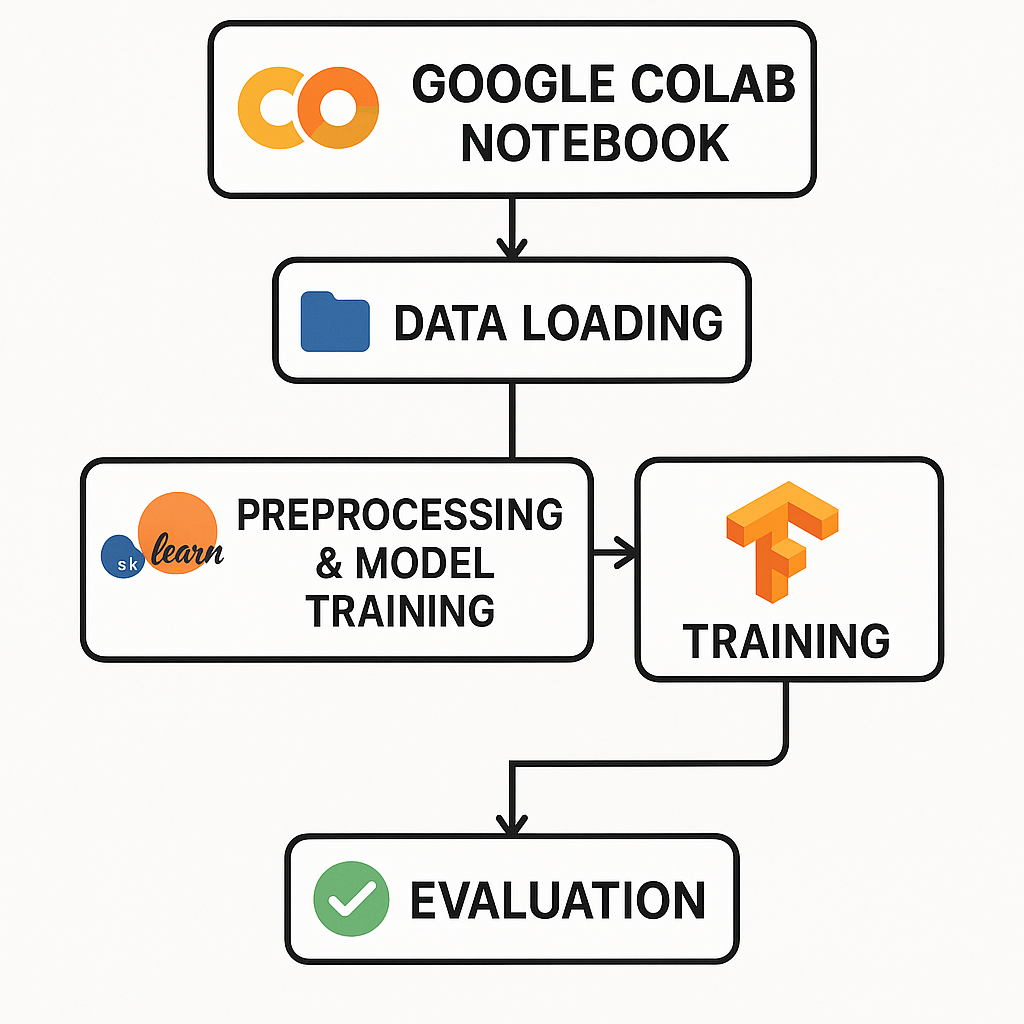
![Workflow diagram of Python implementation in Google Colab with Scikit-learn and TensorFlow]

Workflow diagram of Python implementation in Google Colab with Scikit-learn and TensorFlow
No Google Colab, abra um novo notebook e execute:
!pip install scikit-learn tensorflow matplotlib
Em seguida, importe as bibliotecas:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, ConfusionMatrixDisplay
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers, models
*# Carrega o conjunto Iris*
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X, y = iris.data, iris.target
*# Divide em treino e teste*
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42, stratify=y)
*# Padroniza as características*
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_scaled = scaler.transform(X_test)
*# Cria e treina o modelo*
clf = LogisticRegression(multi_class='ovr', solver='liblinear')
clf.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
*# Faz predições e avalia*
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test_scaled)
acc = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Acurácia (Iris, Logistic Regression): {acc:.2f}")
*# Exibe matriz de confusão*
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
disp = ConfusionMatrixDisplay(cm, display_labels=iris.target_names)
disp.plot(cmap='Blues')
plt.title("Matriz de Confusão - Iris")
plt.show()